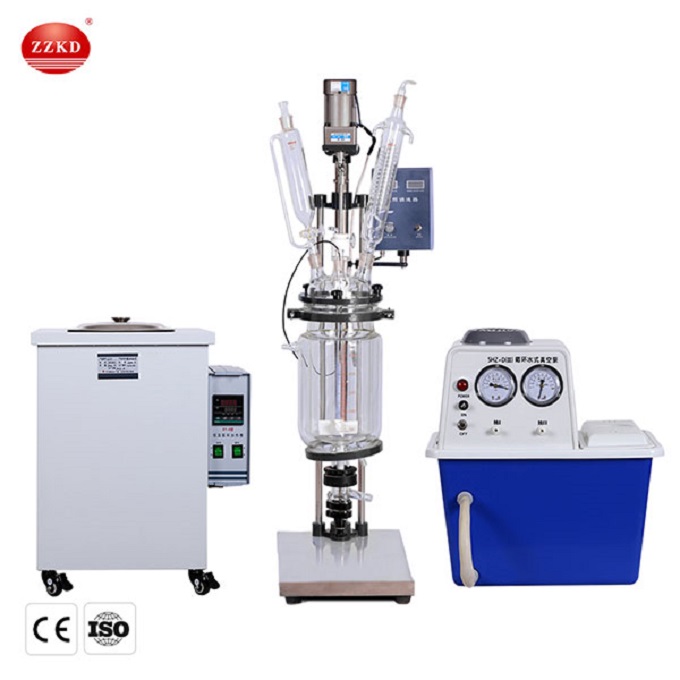
A jacketed glass reactor typically consists of several parts that work together to facilitate chemical reactions and maintain optimal conditions for the process. Here are some of the key parts of a jacketed glass reactor:
Glass Vessel: This is the main body of the 5l jacketed glass reactor, made of high-quality borosilicate glass or another type of glass that is resistant to thermal shock and chemical corrosion.
Jacket: The jacket is a layer surrounding the glass vessel that allows for temperature control of the reaction. Coolant or heating fluid is circulated through the jacket to maintain the desired temperature.
Agitator: Some jacketed glass reactor come with an agitator or stirrer, which is used to mix the reactants and ensure a homogeneous reaction. The agitator can be mechanical or magnetic, depending on the specific application.
Ports: The reactor may have several ports, such as inlet and outlet ports for the coolant or heating fluid, a sampling port, and ports for temperature probes or other sensors.
Flanges and Fittings: The glass vessel may have flanges or fittings for connecting various components, such as the agitator, ports, and jacket.
Clamps: Clamps are used to secure the glass vessel to the stand or frame, providing stability during the reaction.
Cover: The reactor may have a cover or lid to protect the contents from contamination and maintain the desired pressure conditions.
Thermowell: A thermowell is a tube that allows a temperature probe to be inserted into the reactor without exposing it to the reactants.
Temperature Control System: Some jacketed glass reactors come with a temperature control system, which can be used to set and maintain the desired temperature.
Gaskets and Seals: Gaskets and seals are used to prevent leaks and maintain the integrity of the reaction vessel. They are typically made of materials that are resistant to chemical corrosion and can withstand high temperatures.
Stand or Frame: A stand or frame is used to support the reactor and provide stability during the reaction. The stand may be made of metal or another durable material, and may be adjustable to accommodate different reactor sizes.
Condenser: Some jacketed glass reactors come with a condenser, which is used to cool the vapors that are produced during the reaction. The condenser is typically located on top of the reactor and is connected to the glass vessel via a port.
Vacuum Valve: A vacuum valve is used to control the pressure inside the reactor. It allows for the removal of air or other gases from the reactor and can be used to create a vacuum or reduce the pressure during the reaction.
Stirrer Motor: If the reactor has an agitator or stirrer, it will also have a stirrer motor. The motor is used to rotate the stirrer and mix the reactants.
Control Panel: Some jacketed glass reactors come with a control panel, which is used to set and monitor various parameters such as temperature, agitation speed, and pressure.
These are some of the main parts of a jacketed glass reactor, but the exact components may vary depending on the specific reactor model and application. It’s important to carefully evaluate the parts and specifications of a reactor before making a purchase to ensure that it meets your needs and requirements. Additionally, proper maintenance and regular inspection of the parts is important for safe and effective operation of the reactor.