The pace of technological change is accelerating at an unprecedented rate. Emerging technologies like cloud, 5G, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning are driving business innovation and disrupting traditional models. Companies need to adapt quickly to leverage these innovations and prepare for the future.
A culture of continuous learning and skill-building is crucial to develop talent that can harness new technologies. Providing personnel with easy access to innovation resources for the latest technology skills can enable this culture shift. This post explores some of the key technological shifts reshaping businesses and how organizations can foster a culture of learning and experimentation.
The Acceleration Of Technological Change
Major technology shifts are happening now. Innovations like cloud computing, 5G, AI, machine learning, and the metaverse are transforming businesses. They are enabling new products, services, and business models.
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing power. This removes the need for huge upfront infrastructure investments. The flexibility of the cloud allows businesses to easily scale up or down as needed. AI and machine learning add intelligence to products and automate processes to improve efficiency. 5G networks accelerate data transfer with ultra-low latency. Immersive technologies like AR and VR create new human-machine interfaces.
These technologies have big implications for businesses. Products with AI can provide personalized, predictive experiences for consumers. Supply chains can use analytics to forecast demand more accurately. Marketers gain better customer insights to target campaigns. Overall, these technologies make businesses more agile.
However, to benefit, companies need the vision and willingness to embrace change. Too often, organizations stick with legacy systems and processes. To shape the future, businesses must break from the status quo. They need to reimagine not just products and services but also processes, business models, and workplace culture.
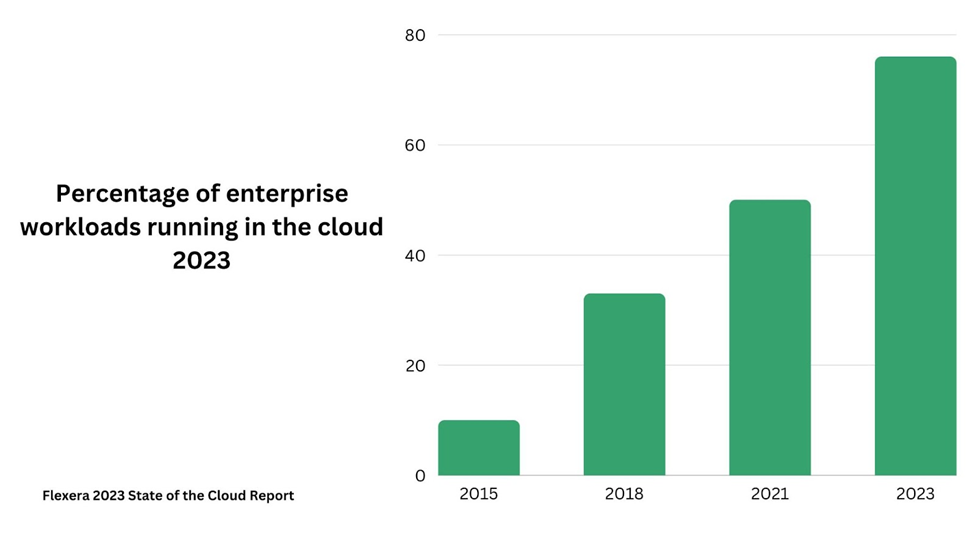
Here is a bar chart showcasing the percentage of enterprise workloads running in the cloud in 2023:
Innovation At The Edge
While the cloud is enabling greater centralization of data and intelligence, there is also a counter-trend towards edge computing. Edge refers to processing data closer to the source, such as on local servers or devices themselves. The growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) and rising demand for low-latency experiences is fueling edge computing innovation.
Edge computing also promises to augment 5G’s potential. With processing on the edge, 5G networks can deliver near real-time experiences by reducing the back and forth between devices and distant servers. For robotics, industrial automation, AR/VR, and autonomous vehicles, 5G and edge computing will work in tandem to share data and drive innovation.
The proliferation of edge devices and 5G will also accelerate the exponential growth in data creation. IDC estimates the global dataspace will grow 61% from 2018 to 2025, reaching 175 zettabytes. With reams of data generated at the edge, AI will play a crucial role in analyzing insights and driving intelligent real-time decision-making.
A Perpetual-Learning Culture
The dizzying pace of technological change means that continuous, lifelong learning is now a requirement to remain competitive. Technical skills have a short half-life today. Programming languages, software frameworks, machine learning models, and cybersecurity threats evolve rapidly.
Organizations need to instill and support a culture of constant experimentation and learning to build future-ready skills. Traditional classroom training is no longer enough. Companies need online, on-demand learning platforms that allow personnel to upskill continuously. Microlearning through bite-sized courses helps employees learn while working.
Role-based learning paths that combine hands-on labs, credentialing, and nano-degrees in domains like cloud, cybersecurity, and AI can bridge competency gaps. Gamified learning adds engagement while virtual labs simulate on-the-job application of skills. The enablement of citizen developers through low-code/no-code platforms also boosts productivity.
HR leaders must understand that learning is now an ongoing journey, not a one-time event. An adaptable and skilled workforce is the foundation for rapid innovation. Technology leaders too need to champion learning and experimentation within teams. With the democratization of technology, the innovation power of an organization extends far beyond the IT department today. Also checkout, when a man tells you about his finances.
IT As A Service
Traditionally, IT departments were the sole custodians of technology within companies. The CIO decided which solutions were adopted, often leading to siloed and incompatible systems. But now companies are increasingly embracing an IT-as-a-service approach to empowering business units.
Small, composable microservices with open APIs are replacing monolithic systems. As a result, business teams can easily integrate solutions tailored to their needs, via cloud marketplaces and SaaS apps. Low-code/no-code platforms also enable citizen developers to build custom applications faster.
IT leaders are evolving from controlling technology to becoming enablers of innovation across the business. IT support in Barnsley provides the technology building blocks and APIs needed for the business to quickly experiment and innovate. They help ensure robust data management, security, and governance while not hindering agility.
This product-centric IT model focuses on maximizing the reuse of capabilities. With cloud-based microservices, redundant development work is avoided while accelerating speed-to-market. IT leaders should view their role as creating a thriving technology marketplace within the company. This empowers business units with the ingredients needed to rapidly innovate to changing customer needs.
Expanded Trust Boundaries
However, as companies embrace new technologies and openness, the risks of cyber threats and data misuse also grow. High-profile hacks and privacy scandals have elevated trust and security as competitive differentiators. Customers today demand transparency into how their data is used. Regulations like GDPR also impose heavy penalties for violations.
Alongside monitoring network traffic and system access, cybersecurity teams now need to track data on the move across an expanded IT perimeter. With remote work and bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies, sensitive data is more dispersed than ever. As edge computing spreads, securing a multitude of IoT devices becomes vital too.
Leading companies recognize that privacy and security must be baked into products and processes from the initial design stage. Responsible AI practices that avoid bias and ensure transparency are crucial in building user trust. Robust consent and preference management enable personalized experiences while honoring customer choices.
Trust is now a critical business metric, not just an IT issue. The technology leaders who proactively monitor privacy and security risks will be best positioned to enable innovation and growth.
Key Takeaways
- Emerging technologies like cloud, 5G, and AI are accelerating business innovation but require organizations to be agile and willing to transform legacy systems.
- Edge computing is gaining traction and will need to be integrated with the cloud and 5G networks to enable real-time experiences.
- A culture of continuous learning and skill-building is crucial to develop talent that can harness new technologies.
- IT needs to transition from controlling technology to becoming an enabler of innovation by providing easy-to-use building blocks.
- With open ecosystems, trust and security are now enterprise-wide responsibilities needing proactive risk monitoring.
The future will belong to bold organizations that embrace a culture of perpetual learning, tap into collective knowledge, and proactively address emerging risks. Technology leaders who provide an open but secure innovation platform will power business success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, innovation is crucial for businesses to stay relevant in an ever-evolving landscape. While traditional resources like R&D and new talent acquisition remain key drivers, companies must also tap into emerging sources of innovation. By leveraging advancements in technology, optimizing knowledge management, encouraging a startup culture, and fostering strong collaboration, businesses can successfully reshape their capacity for innovation. This agile approach will enable companies to continuously deliver new value propositions, disrupt markets, and ultimately future-proof their organization. The future belongs to those who can harness the full spectrum of innovation resources.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How can companies keep up with emerging technologies?
Adopt cloud-based solutions for increased agility, invest in continuous skill development, and create a culture of learning and innovation. Appoint dedicated scouting teams to identify emerging tech with business potential.
2. What is the role of data in the future of business?
Data is rapidly becoming the lifeblood of organizations. Companies need strong data governance while leveraging analytics and AI to glean insights that drive innovation. Edge computing will accelerate data generation.
3. How can IT departments facilitate innovation?
IT needs to transition from controlling technology to providing easy-to-integrate solutions. Focus on reusable microservices, open API, and empowering citizen developers. Create enterprise app stores with pre-approved solutions.
4. How can businesses balance innovation with privacy?
Make trust and privacy a priority across divisions. Appoint dedicated data stewardship teams, utilize technologies like differential privacy and federated learning, and be transparent about data practices.
5. What skills do employees need to thrive in the future?
Focus on adaptability, tech literacy, continuous learning, creativity, and collaboration. Look for potential over demonstrated expertise. Foster growth mindsets over fixed skills.