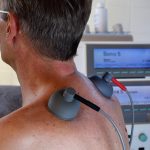
The positive effects of heat and cold on pain and certain diseases have been known for centuries. The heat treatment is a widely used method for treating pain and not inflammatory diseases.
Other areas of application include colds, flu, muscle tension, or abdominal pain. Numerous treatment methods ensure that the body or a specific area (e.g., back, joints) is supplied with heat.
The cold therapy is usually performed for acute and painful illnesses. For example, it is used for treating bleeding, swelling, or inflammation in the form of ice pouring, baths, or other methods. Check Ortho Bracing for better understand on cold therapy.
Even if many people find warmth or cooling off to be beneficial and therefore see it as “helpful in all situations.” You should note that high or low temperatures are of little use in certain diseases and can also be harmful in some cases.
Examples may include conditions such as inflammation of the internal organs but also many other serious complications.
Cold therapy is not suitable for urinary tract infections, period pain, or inflammatory rheumatism.
But, when each therapy is the right choice? In the following lines, we will tell you a bit more about each of them and how you can both of them more safely.
Cold therapy as the quickest relief from injuries
Cold therapy takes advantage of the fact that blood vessels contract during cold stimuli and the muscles become tense. As soon as the cold stimulus is no longer there, the muscles relax, and a warm feeling arises for a few minutes.
That is why everyone who obtains a knee injury finds the most exceptional comfort in using a knee ice pack that entirely surrounds the swollen area with the right cold temperature.
Since the cold-sensitive nerves transmit their information to the brain faster than the pain-conducting nerve pathways, cold often relieves pain.
Moreover, ice acts as a potent local anti-inflammatory agent. The reason is that the cold generates vasoconstriction, which is associated with a progressive decrease in local temperature. And consequently, with a reduction in inflammation and exudate.
Besides, if the cold is applied as soon as the injury originates. The chemical mediators that generate the inflammation will be terminated.
Heat therapy to increase the blood flow and quicken the recovery
The basis of heat therapy is that the blood vessels dilate when the heat is applied, thus promoting blood circulation. In this way, the muscles relax, and the nerve pathways are relieved.
A prominent dental practice in Beaconsfield advises that the temperature-sensitive nerve endings transmit the positive heat stimuli to the pain center. This triggers chemical processes that additionally dampen the sensation of pain.
The supply of heat also has a positive effect on the production of stress hormones and stimulates cell metabolism.
The heat therapy can be carried out in different ways. A common form is hot baths. These serve to supply the body with more heat than it can generate itself. This stimulates the immune system, and the body temperature rises.
This change in temperature is said to help the body kill pathogens. Since organic and mineral substances such as bog, clay, and earth store the heat for an unusually long time, these materials are often used in heat therapy in the form of packs or wraps.
These packs are put on for about 45 minutes. Mud or mud baths are used for full body treatment. To increase the effect, you should rest covered for another 30 minutes after treatment.
There are numerous ways to use both cold and heat therapy to your advantage
In the cold therapy pourings, baths and showers change applied in the temperature range of 12 °C to 15 °C. Other therapy options include walking barefoot through rope or snow.
Other types of cold therapy are ice packs, and gel compresses. Ice pack for back pain provides an effective and safe way to reduce inflammation and soreness. By having the cold pack on for a longer period of time, the blood vessels in the skin constrict and the circulation to the area decreases. This helps to reduce the amount of inflammation and pain in the back.
The use of gel compresses is also an effective cold therapy for back pain. These compresses can provide longer-lasting relief than ice packs and are easy to use. They are placed directly on the affected area and can provide a cooling sensation that can help reduce the pain.
Wrapped in a cloth, they usually remain on the skin for only a few minutes. After a short warm-up phase of the skin, the cold treatment with compresses can be repeated a total of four to five times.
The alternating use of heat and cold, which is known in Asia as a sweat lodge and in Northern Europe as a sauna, which is another fantastic therapeutic solution. It serves to clean the tissues, harden the body, and improves the circulation and muscles as well as the whole immune system.
Areas of application for heat therapy include:
- Abdominal pain
- Sciatica
- Muscle tension
- Neuritis
- Joint pain
- Kidney and bladder problems
Cold therapy can help with swelling, bruising, and acute pain. Both methods are therapy methods recognized by science and health insurers.
Basically, there is a risk that the circulatory system will be overloaded with heat therapy. Symptoms can range from headaches and nausea to fainting. To avoid this, you should cool the body with cold water at the first sign of these side effects.
Diabetics should seek medical advice before undergoing heat treatment, as the temperature sensation is often disturbed in this disease. This can lead to a misjudgment of the thermal stimuli, which could result in burns. Heat applications after exercise or large meals are also not advisable.
In the case of diseases such as tuberculosis, cancer, epilepsy, and inflammation of the internal organs, heat treatment should also not be carried out, as the condition may possibly be aggravated.
Heat therapy also is not recommended for:
- People with urinary tract Infections
- Irritable bladder
- Sciatica
- Inflammatory rheumatism
- Menstrual cramps
Heat therapy also is not recommended for:
- People who have frequent problem with cold hands,
- Debility,
- High blood pressure,
- Catarrh,
- Heart disorders,
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland,
- Increased intraocular pressure (glaucoma)
In conclusion
Consult with your family doctor or pharmacist before you treat yourself with heat therapy or cold therapy.
This not only makes sense to find the right method – but the doctor can also determine, for example, what is behind the symptoms and prescribe a more appropriate therapy if necessary.
Diabetics and other people with whom the temperature sensation is disturbed should only undertake heat and cold applications under medical supervision to avoid burns or frostbite.